SQL Server TempDB is a special database in SQL Server that stores temporary objects. It allows you to partition your workloads such that frequently accessed data is stored in memory and less frequently accessed data can be stored on disk, reducing contention for resources. It not only provides you temp storage but also helps improve the performance of the database queries and reduces workloads of the front-end applications as well.
You rarely use TempDB directly, but it has many functions behind the scenes and it is always in use by SQL Server to ensure the performance and responsiveness of some system and non-system databases. For example, if a database operation is too large that needs more memory and storage than the database server currently has, the server uses TempDB as the temp storage to help execute the operation. You can think of TempDB as virtual memory and storage on the OS level that is used when Windows OS needs extra memory and storage.
What is SQL Server TempDB
TempDB is a system database used by SQL Server (and other RDBMS).
Apps requiring heavy sorting, grouping, etc. can use TempDB to offload temporary data.
TempDB files are recreated every time SQL Server starts, so the data in them will be lost after a restart.
You can use TempDB to store your custom tables, query results, views, and variables.
What is stored in TempDB?
TempDB is a system database. Its name is derived from the fact that it stores temporary user objects. These are tables, stored procedures, table variables, cursors, or derived tables that contain intermediate results when processing queries.
SQL Server uses the TempDB database for various purposes such as the storage of temporary user objects like tables, temporary stored procedures, table variables, cursors, or derived tables that contain intermediate results when processing queries and for internal SQL Server system objects such as row versioning information.
This database is used for sorting and grouping large amounts of data during the execution of a query. It can also be used for storing rows returned by an INSERT statement in batches (one batch per thread). The size of each row varies but is usually 8 KB or 16 KB for small tables and large rows respectively. For example: If you are inserting a million rows into your table with 100 columns each then you would have 100 million pages in tempdb.*
How to access TempDB?
The TempDB is a system database and in automatically created when a SQL Server is installed on a machine. You can access TempDB object by executing queries on TempDB or using SSMS.
Let’s look at the SSMS system databases installed by default when a new SQL Server is installed. As you can see from the following image, four system databases are installed by default when a new SQL Server is installed, master, mode, msdb, and tempdb.
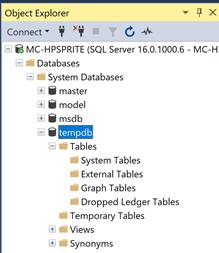
If you expand tempdb database, you will see Tables, Views etc. However, until you start working with databases, they all will be empty.
Where is TempDB location?
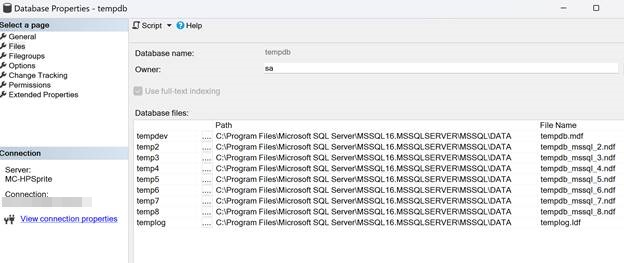
The default location of tempdb database is the data folder same where other system databases are. If you right click on tempdb in SSMS, select Properties and select Files, you can find the exact location of tempdb.mdf and other supporting files. The templog file is also in the same folder.
How to move TempDB to a Different Drive or Folder?
Often times, we do not want to store tempdb data and log files on our main drive. You can change the default location of tempdb data and log files by moving them to another drive or folder using the ALTER DATABASE statement.
Run the following command on tempdb.
ALTER DATABASE [tempdb] MODIFY FILE ( NAME = N'tempdev', FILENAME = N'D:\tempdbstorage\tmp.mdf');
GO
ALTER DATABASE [tempdb] MODIFY FILE ( NAME = N'templog', FILENAME = N'D:\tempdbstorage\tmplog.ldf');
GO
Once you execute the above queries, Stop and Restart SQL Server service to make this change in effect.
Also, don’t forget to delete old tempdb.mdf and templog.ldf files.
How to create a Temporary Table in TempDB?
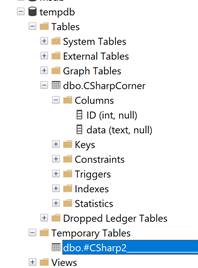
We can also use tempdb explicitly by createng tables, views etc on a tempdb. We can also create regular table as well as temp tables. The following queries create two tables in tempdb, CSharpCorner and Csharp2.
CREATE TABLE CSharpCorner (ID int, data text);
CREATE TABLE #CSharp2 (ID int, name text);
Select tempdb in SSMS and execute above queries in query explorer on tempdb. Right click on tempdb, select New Query, type above SQL statements and execute.
Now refresh tempdb, Right click on tempdb, select Refresh.
Expand Tables and Temporary Tables nodes.
You will CSharpCorner tabe and CSharp2 temporaty table in the database.
To learn how to work with temproraty tables, read Working with Temporaty Tables in SQL Server.
The tempdb is also used to store Temporary Variables. Temporary Variables are used to store data temporarily in tempdb.
Apps requiring heavy sorting, grouping etc. can use TempDB to offload temporary data
You can use TempDB to offload temporary data from the transactional tables. For example, if you are writing an OLTP application that requires heavy sorting and grouping operations, you can use TempDB to store these temporary results.
Sorting or grouping is a common operation when you are processing large amounts of data in a relational database. However, sorting is one of the most expensive operations in traditional databases because it involves disk I/O as well as CPU utilization by the query processor (SQL Server).
TempDB files are recreated every time SQL Server starts.
The TempDB is a system database. It's not specific to any SQL Server instance, but it's always created when you start SQL Server.
For this reason, TempDB is recreated every time SQL Server starts. This happens regardless of whether it was dropped or not, and also if the files are manually deleted (but not using RECREATE).
If TempDB is on an SSD it performs better compared with HDD
If the TempDB database is on an SSD, it performs better compared with a HDD. SSDs are faster, more reliable and durable than HDDs, but they are also more expensive.
TempDB should be one single file per core - up to 8 cores.
SQL Server recommends that TempDB be one single file per core - up to 8 cores. The number of cores in a server can be determined by using the following query:
SELECT * FROM sys.dm_os_sys_info WHERE name='max degree of parallelism'
To determine the number of associated data files for an instance, you can use this script:
select * from sys.master_files
You can monitor TempDB usage using sys.dm_db_task_space_usage and sys.dm_exec_query_resource_semaphores DMVs.
In general, you can monitor TempDB usage using sys.dm_db_task_space_usage and sys.dm_exec_query_resource_semaphores DMVs.
sys.dm_db_task_space_usage: This DMV returns information about the memory used by all user processes that are connected to the instance of SQL Server. The information includes a breakdown of how much memory each process is using in its buffers, as well as whether any allocations have been deferred or not yet committed by a specific session.
sys.dm_exec
exec (sqlserver) This function returns a recordset object that represents an execution plan for an SQL statement compiled with the specified options and parameter values—or no such plan if there is none available because of insufficient system resources or incompatible settings on this instance of SQL Server2005 2005 Management Studio (SSMS).
How to distribute TempDB files for better performance?
When multiple tempdb files are used, make sure they are evenly distributed across different physical disks to improve performance and reliability (e.g., by putting the tempdb files on separate physical disks).
When monitoring the performance of SQL Server, look at the disk I/O subsystem performance. If a disk is reached its maximum throughput, it becomes the bottleneck for SQL Server's workload. If you experience lower than expected CPU utilization, it may indicate that your I/O subsystem is limiting your system’s overall performance instead of CPU resources being consumed by other tasks such as data compression or encryption operations running concurrently with other workloads.
HostForLIFEASP.NET SQL Server 2019 Hosting
