One of the most potent database management systems for storing and retrieving data is SQL Server. The DBAs are occasionally unable to access the database because of its "Recovery Pending" state. This article's goal is to explain why it happens and provide suggestions for resolving the problem.
If one or more of the core files in a SQL database are corrupted, the database is considered damaged. The database will be marked with various states based on how serious the problem is. Among these states are:
- Online: If a database data file is damaged during query execution, it will stay online.
- Suspect: A database will be marked as a "suspect" if it cannot be recovered during SQL Server initialization.
- Recovery Pending: The SQL Server places the database in a "Recovery Pending" state if it knows that a recovery needs to be done but is unable to begin due to an issue.
What Does SQL Server Recovery Pending State Mean?
The Recovery Pending state in MS SQL Server indicates that the database cannot start the recovery process due to missing files, resource constraints, or corruption issues. This is different from the Suspect state, which clearly shows there is corruption. Recovery Pending just means the recovery can't continue due to incomplete or inconsistent files.
Common Causes of SQL Server Recovery Pending State
- Insufficient Disk Space: The database recovery process may halt due to a lack of space on the server.
- Corrupted Log Files: Damaged or missing transaction log files can disrupt recovery.
- Power Failure or Crash: Unexpected shutdowns can lead to database inconsistency.
- Hardware Malfunctions: Disk errors or faulty storage devices can corrupt database files.
- Improper Shutdowns: Forceful termination of SQL Server processes can result in uncommitted transactions.
When a database is in this state, it becomes inaccessible, and immediate action is required to restore normal operations.
How Does SQL Server Recovery Work?
When an SQL Server starts or a database is restarted, it goes through a recovery process with three phases:
- Analysis: SQL Server reads the transaction log to determine which transactions need to be rolled forward or rolled back.
- Redo (Roll Forward): All committed transactions from the log are reapplied to the database to ensure consistency.
- Undo (Roll Back): Uncommitted transactions are rolled back to maintain a clean state.
Characteristics of a Database in the "Recovery Pending" State
- Database Inaccessible: The database is not available for use by applications or users.
- No Automatic Recovery: SQL Server is unable to initiate the automatic recovery process.
- Error Messages: Common error messages related to this state include:
- Error 9003: The log file is corrupt or missing.
- Error 1813: SQL Server cannot attach the database because some files are missing.
- Error 5123: The operating system returned an error while trying to access the database files.
How to Check if a Database is in Recovery Pending State?
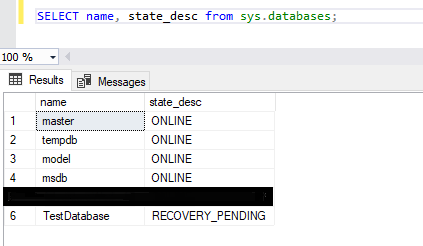
To verify the state of your SQL Server database, execute the below query:
SELECT name, state_desc FROM sys.databases;
This query lists all databases and their current states. If the database is marked as "RECOVERY_PENDING" you need to fix the issue.
Methods to Fix SQL Server Recovery Pending State
1. Ensure Sufficient Disk Space: First, check if the drive with the database files has enough free space. If not, free up some space or move the files to a drive with more storage.
2. Check SQL Server Permissions: Make sure the SQL Server service account has the right permissions to access the database files. Wrong permissions can block the recovery process.
3. Manually Bring the Database Online: You can attempt to resolve the issue by setting the database to Emergency mode and performing repairs. Follow these steps:
Set the Database to Emergency Mode:
ALTER DATABASE [TestDatabase] SET EMERGENCY;
Perform Consistency Check: Run DBCC CHECKDB to check for corruption:
DBCC CHECKDB([TestDatabase]);
Repair the Database: If corruption is detected, use the REPAIR_ALLOW_DATA_LOSS option to repair the database:
ALTER DATABASE [TestDatabase] SET SINGLE_USER;
DBCC CHECKDB([TestDatabase], REPAIR_ALLOW_DATA_LOSS);
ALTER DATABASE [TestDatabase] SET MULTI_USER;
Note: The REPAIR_ALLOW_DATA_LOSS option may result in some data loss. Always back up your database before using this option.
4. Restore from a Backup: If you have a recent backup of the database, restoring it can be the safest way to resolve the issue:
RESTORE DATABASE [TestDatabase] FROM DISK = 'BackupFilePath.bak';
5. Use third-party recovery tool: When there are problems with SQL Server, like database corruption or the "Recovery Pending" state, manual troubleshooting methods, such as restoring from backups, running DBCC CHECKDB, or detaching and reattaching database files, may not always help. In these situations, special tools like Stellar Repair for MS SQL can be very important for recovering essential data accurately and quickly. In situations where data is accidentally deleted, specialized recovery techniques can help retrieve the deleted records during the database repair process, ensuring that important information is not permanently lost.
How SQL Database Repair Tools Can Assist in Recovery?
- Repair tools help fix corrupted MDF and NDF files and restore the database without changing its original structure..
- The tool can bypass the issues and recover the data even if SQL Server cannot bring it online.
- Unlike manual methods that may risk losing data, the recovery process ensures no data loss..
- Whether you are using an old or the latest version, the tool supports all versions and ensures smooth recovery.
- In situations where data is accidentally deleted, specialized recovery techniques can help retrieve the deleted records during the database repair process, ensuring that important information is not permanently lost.
Preventive Measures
- Regularly back up your database to avoid data loss during unforeseen issues.
- Monitor disk usage and ensure sufficient free space.
- Use reliable storage devices to minimize hardware-related corruption.
- Always shut down SQL Server gracefully to prevent uncommitted transactions.
Conclusion
To fix a SQL Server database in a 'Recovery Pending' state, you need to find the root cause and take the right steps. Manual fixes like repairing the database or restoring from backups can help, but may not work for heavily corrupted databases. Always keep regular backups and check disk space to avoid these problems.
HostForLIFEASP.NET SQL Server 2022 Hosting
