In this post, I will tell you about the LAG and LEAD functions in SQL Server. These two functions are analytical functions in SQL Server. In actual scenarios we need to analyze the data, for example, comparing previous sales data.

The Lag and Lead functions support the window partitioning and ordering clauses in SQL Server. The Lag and Lead functions do not support the window frame clause.
LAG
The Lag function gives the previous column values based on ordering.
LEAD
The Lead function gives the next column values based on ordering.
Demo
CREATE TABLE DBO.SALES
(
PROD_ID INT ,
SALES_YEAR INT,
SALES_AMOUNT INT
)
INSERT INTO DBO.SALES(PROD_ID,SALES_YEAR,SALES_AMOUNT) VALUES(1,2009,10000)
INSERT INTO DBO.SALES(PROD_ID,SALES_YEAR,SALES_AMOUNT) VALUES(1,2010,9000)
INSERT INTO DBO.SALES(PROD_ID,SALES_YEAR,SALES_AMOUNT) VALUES(1,2011,8000)
INSERT INTO DBO.SALES(PROD_ID,SALES_YEAR,SALES_AMOUNT) VALUES(1,2012,7000)
INSERT INTO DBO.SALES(PROD_ID,SALES_YEAR,SALES_AMOUNT) VALUES(1,2013,14000)
INSERT INTO DBO.SALES(PROD_ID,SALES_YEAR,SALES_AMOUNT) VALUES(1,2014,18000)
INSERT INTO DBO.SALES(PROD_ID,SALES_YEAR,SALES_AMOUNT) VALUES(1,2015,15000)
INSERT INTO DBO.SALES(PROD_ID,SALES_YEAR,SALES_AMOUNT) VALUES(2,2013,12000)
INSERT INTO DBO.SALES(PROD_ID,SALES_YEAR,SALES_AMOUNT) VALUES(2,2014,8000)
INSERT INTO DBO.SALES(PROD_ID,SALES_YEAR,SALES_AMOUNT) VALUES(2,2015,16000)
INSERT INTO DBO.SALES(PROD_ID,SALES_YEAR,SALES_AMOUNT) VALUES(3,2012,7000)
INSERT INTO DBO.SALES(PROD_ID,SALES_YEAR,SALES_AMOUNT) VALUES(3,2013,8000)
INSERT INTO DBO.SALES(PROD_ID,SALES_YEAR,SALES_AMOUNT) VALUES(3,2014,9700)
INSERT INTO DBO.SALES(PROD_ID,SALES_YEAR,SALES_AMOUNT) VALUES(3,2015,12500)
SELECT * FROM DBO.SALES

The following example shows the Previous Year Sales Amount.
SELECT *, LAG(SALES_AMOUNT) OVER(ORDER BY PROD_ID ,SALES_YEAR) [Prevoius Year Sales] FROM DBO.SALES

The following example shows the Next Year Sales Amount.
SELECT * ,
LEAD(SALES_AMOUNT) OVER(ORDER BY PROD_ID ,SALES_YEAR) [Next Year Sales]
FROM DBO.SALES

The following example shows the Previous Year Next Year Sales Amount using the partition by clause.
SELECT *,
LAG(SALES_AMOUNT) OVER(PARTITION BY PROD_ID ORDER BY PROD_ID ,SALES_YEAR) [PREVOIUS YEAR SALES] ,
LEAD(SALES_AMOUNT) OVER(PARTITION BY PROD_ID ORDER BY PROD_ID ,SALES_YEAR) [NEXT YEAR SALES]
FROM DBO.SALES

The following example shows an offset other than 1.
The offset is by default 1. If we want an offset other than 1 then we need to provide 2 argument values in the Lag and Lead functions.
SELECT * ,
LAG(SALES_AMOUNT,2) OVER(ORDER BY PROD_ID ,SALES_YEAR) [PREVOIUS YEAR SALES] ,
LEAD(SALES_AMOUNT,2) OVER( ORDER BY PROD_ID ,SALES_YEAR) [NEXT YEAR SALES]
FROM DBO.SALES

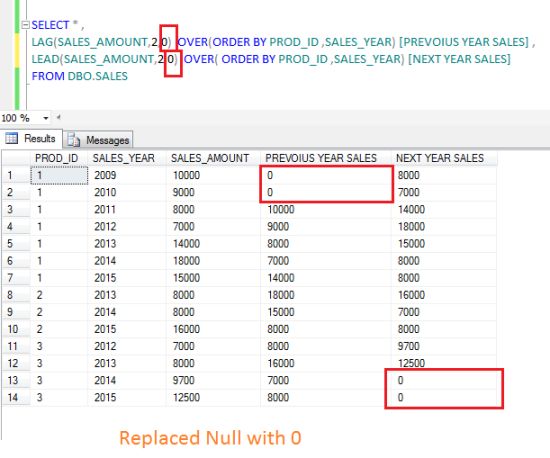
The following example shows replacing the null with various values:
SELECT * ,
LAG(SALES_AMOUNT,2,0) OVER(ORDER BY PROD_ID ,SALES_YEAR) [PREVOIUS YEAR SALES] ,
LEAD(SALES_AMOUNT,2,0) OVER( ORDER BY PROD_ID ,SALES_YEAR) [NEXT YEAR SALES]
FROM DBO.SALES
HostForLIFE.eu SQL Server 2016 Hosting
HostForLIFE.eu is European Windows Hosting Provider which focuses on Windows Platform only. We deliver on-demand hosting solutions including Shared hosting, Reseller Hosting, Cloud Hosting, Dedicated Servers, and IT as a Service for companies of all sizes.
